运行时加载
动态链接库提供的API
函数声明
/* Open the shared object FILE and map it in; return a handle that can be
passed to `dlsym' to get symbol values from it. */
extern void *dlopen (const char *__file, int __mode) __THROWNL;
/* Unmap and close a shared object opened by `dlopen'.
The handle cannot be used again after calling `dlclose'. */
extern int dlclose (void *__handle) __THROWNL __nonnull ((1));
/* Find the run-time address in the shared object HANDLE refers to
of the symbol called NAME. */
extern void *dlsym (void *__restrict __handle,
const char *__restrict __name) __THROW __nonnull ((2));
/* When any of the above functions fails, call this function
to return a string describing the error. Each call resets
the error string so that a following call returns null. */
extern char *dlerror (void) __THROW;
常量
/* The MODE argument to `dlopen' contains one of the following: */
#define RTLD_LAZY 0x00001 /* Lazy function call binding. */
#define RTLD_NOW 0x00002 /* Immediate function call binding. */
#define RTLD_BINDING_MASK 0x3 /* Mask of binding time value. */
#define RTLD_NOLOAD 0x00004 /* Do not load the object. */
#define RTLD_DEEPBIND 0x00008 /* Use deep binding. */
/* If the following bit is set in the MODE argument to `dlopen',
the symbols of the loaded object and its dependencies are made
visible as if the object were linked directly into the program. */
#define RTLD_GLOBAL 0x00100
/* Unix98 demands the following flag which is the inverse to RTLD_GLOBAL.
The implementation does this by default and so we can define the
value to zero. */
#define RTLD_LOCAL 0
/* Do not delete object when closed. */
#define RTLD_NODELETE 0x01000
GNU Inline Assembler(内联汇编)
基础内联汇编
语法
asm asm-qulifiers ( AssemblerInstructions)
在c语言中,关键字asm是GNU拓展的。(不使用GNU拓展的话就用__asm__,但需要添加一些编译选项。)
Qualifiers有两种,volatile和inline,基础内联汇编代码默认都是volatile,显示添加没什么影响就看着好看。
inline的作用文档里说的目前看不懂。
AssemblerInstructions是一个字符串,里面是汇编代码,GCC不会解析这些字符串代表的指令,直接交给assmbler处理,字符串里面可以有多个指令,按照所使用的汇编语法去分割。
Extended Asm - Assembler Instructions with C Expression Operands
Extended asm可以把汇编代码和c代码联系在一起,使用冒号:做分割符。
语法
asm asm-qualifiers (AssemblerTemplate
: OutputOperands
[ : InputOperands
[ : Clobbers] ])
asm asm-qualifiers (AssemblerTemplate
: OutputOperands
: InputOperands
: Clobbers
: GotoLabels)
Qualifiers
volatile
禁止编译器优化
inline
(暂时看不懂)
goto
允许汇编代码跳到c的label
参数
Assembler Template
c编译器会做一些字符串的格式化
特殊的转义字符
%%:产生汇编代码中的一个%
%=、%{、%|、**%}**暂时用不到
输出操作符
格式是这样
[[asmSymbolicName]] constraint (cvariablename)
asmSymbolicName
可以用汇编里面定义的变量名(没用过),没有定义这个后面就会按顺序使用%0,%1这些占位符
constraint
先带一个prefix,再带一个additional constraints,用法挺复杂,常用的有
prefix:=表示overwrirte, +表示读写
additional constraints:r表示register,m表示memory
cvariablename
指定c变量
输入操作符
和输出操作符差不多,只是最后变量变成了表达式,也就是可以用一些函数
Clobbers
没用到
GotoLabels
没用到
函数的调用过程
了解自己系统的汇编代码
因为ABI很多,所以汇编代码得完全根据自己的机器来,我一开用《程序员的自我修养》里面的实例代码跑不通,后来想通了得自己看一下自己电脑上编译出来的汇编代码是什么。
先写一个测试程序
/*test.c*/
#include <stdio.h>
void foobar(int i)
{
printf("foobar %d", i);
}
int main()
{
asm volatile("nop");
foobar(2);
asm volatile("nop");
}
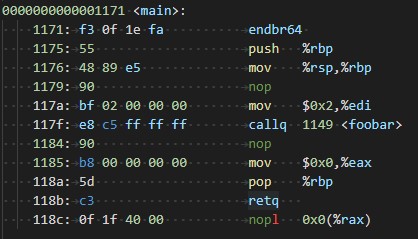
用nop做占位符可以很方便地找出关键代码,可以看到在我地机器上,main函数先往edi寄存器里写了一个2然后就调用foobar了,再来看看foobar里做了什么。
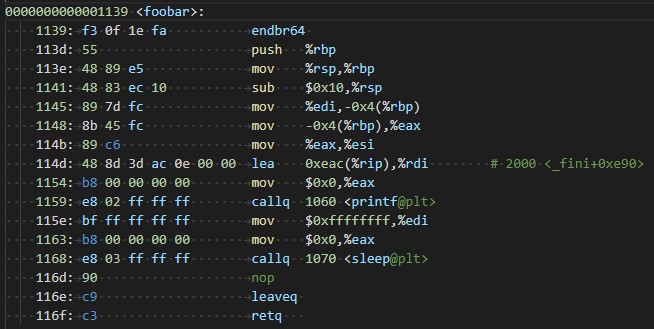
一开始地三连击很熟悉,push,mov,sub,接下来从edi里读出值压入堆栈
所以很明显我的机器上,调用方调用函数之前只要把数值放入edi就行了
/*runso.c*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
while (1)
{
void *handle;
char *error;
int i;
long esp = 0;
void *func;
handle = dlopen("./dynamicLoad/bin/LibB.so", RTLD_NOW);
if (handle == 0)
{
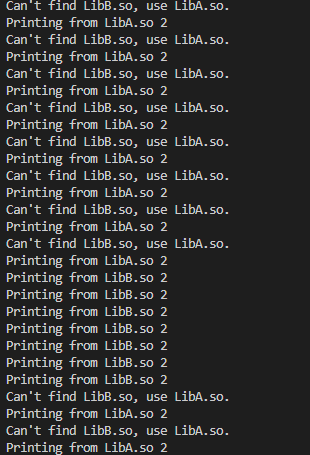
printf("Can't find LibB.so, use LibA.so.\n");
handle = dlopen("./dynamicLoad/bin/LibA.so", RTLD_NOW);
if (handle == 0)
{
printf("Can't find LibA.so,check out ./dynamicLoad/bin/ .");
return -1;
}
}
func = dlsym(handle, argv[1]);
void (*func_void)() = func;
asm volatile("mov %0,%%edi" ::"r"(2));
func_void();
dlclose(handle);
sleep(2);
}
}
/*Lib.c*/
#include <stdio.h>
void foobar(int i)
{
printf("Printing from LibA.so %d\n", i);
sleep(-1);
}